Can a large dog live 20 years

How Long Do Dogs Live?
When it comes to knowing how old your dog is, calculating dog years just doesnt cut it anymorestudies show that a dogs lifespan can vary significantly with breed and size, and there are other factors at play that we still dont fully understand.
Theres a lot to know about the dog lifespan. So if you ever look at your pup and wonder, how long do dogs live? heres how you can estimateand how you can ensure your best friend is around for as long as possible.
The Average Dog Lifespan
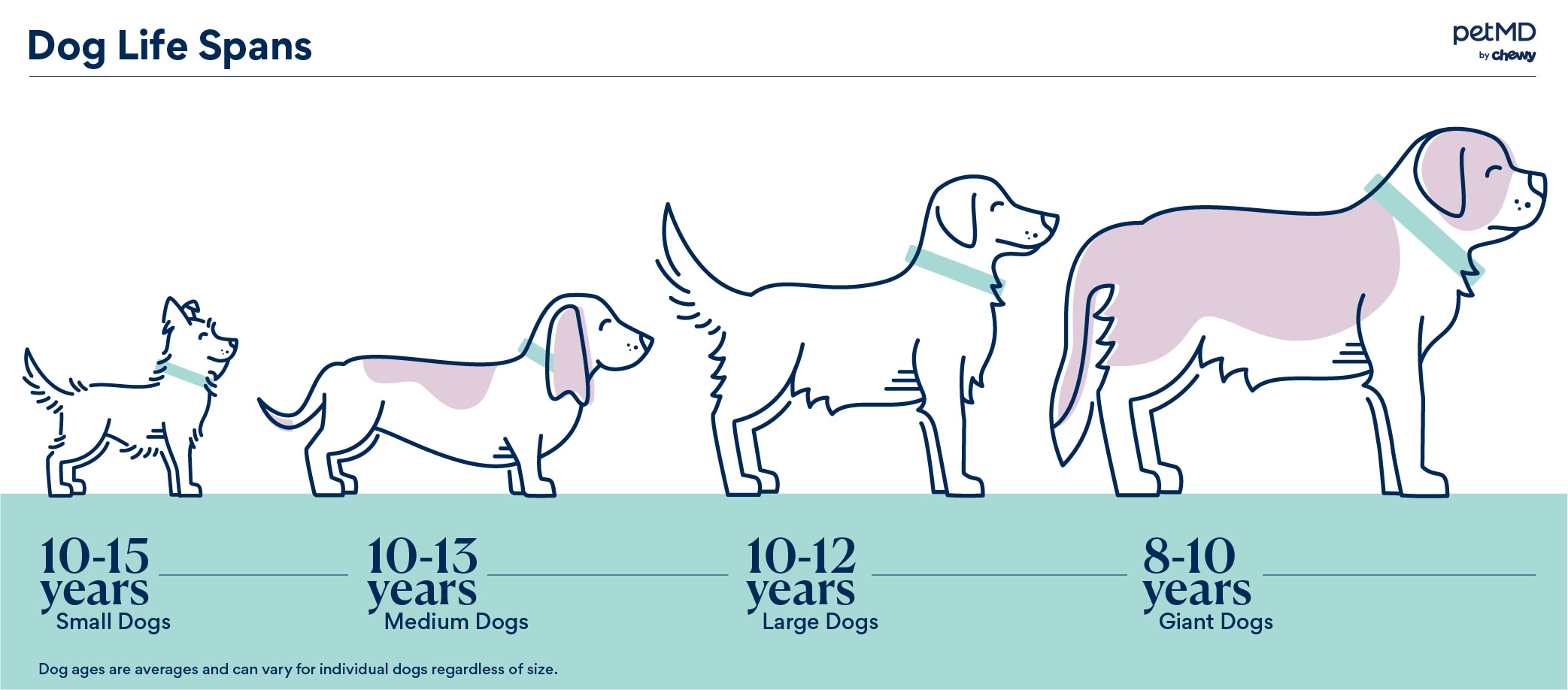
The average lifespan for dogs is between 1013 years, though there is variability among breeds and sizes. As a species, the domestic dog is incredibly diverse in size, build, and appearance, thanks to human intervention. So its no wonder that there are significant differences in the lifespan of a Chihuahua versus a Great Dane.
In general, smaller dog breeds live longer than larger dog breeds. The cause for this is not well established; normally, smaller mammal species have shorter lifespans than larger ones. One possible reason might be that common medical conditions that dogs acquire as they age (such as incontinence and mobility issues) may be more difficult to manage in larger dogs and lead to euthanasia sooner. There also seem to be some differences in the types of illnesses experienced by different-sized breeds.
Genetics also play a huge role in life expectancy for dogs. Purebred dogs are more at risk for specific hereditary diseases because they are bred by other dogs with similar genes. Mixed-breed dogs have a reduced risk of these diseases, which likely contributes to their increased lifespan. Certain breeds are also purposefully bred to have traits that, as an unfortunate result, may also lead to shortened lifespans. For example, brachycephalic dogs such as the English Bulldog are more prone to heatstroke and respiratory-related death due to their small trachea.
The average lifespan for dogs is between 1013 years, though there is variability among breeds and sizes.
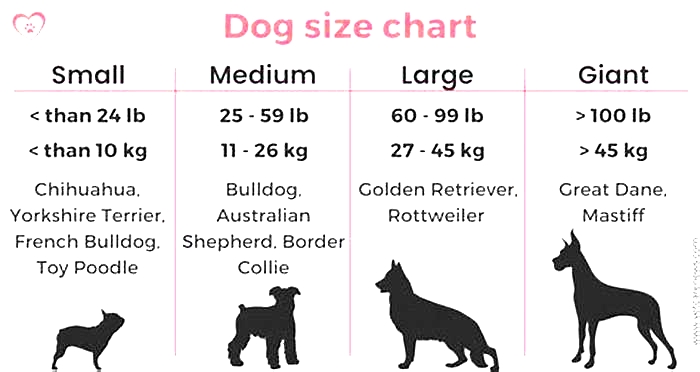
How Long Do Small Dogs Live?
Small-breed dogs tend to have the longest lifespan, averaging 1015 years. But as these long-life dogs age, they are more prone to liver, kidney, and adrenal disease, as well as degenerative heart disease. Small dogs are also very prone to dental disease, which can complicate these other illnesses.
Here are some popular small dog breeds and their average lifespans:
How Long Do Medium-Size Dogs Live?
Medium-size dogs align more with the overall average dog lifespan of 1013 years. But some medium-size dogs can be very long-lived; the oldest dog on record was aRafeiro do Alentejo named Bobi, who lived to be 31 years old!
Medium-size dog lifespans and diseases of concern vary from breed to breed. Bulldogs, for example, are often plagued with health issues due to their snub-nose design, while the hardworking Australian Shepherd has fewer genetic disease predispositions and can live to be 15 or older.
Here are some popular medium-size dog breeds and their average lifespans:
How Long Do Large Dogs Live?
Large-breed dogs have a slightly shorter lifespan than medium breed dogs, at 912 years. Again, these lifespans are heavily affected by breed.
As dogs get larger, they are more likely to be affected by difficult-to-manage arthritis and certain types of cancer. Popular breeds like the Golden Retriever and Bernese Mountain Dog are particularly prone to cancer.
Here are some popular large dog breeds and their average lifespans:
How Long Do Giant Dogs Live?
Towering giant-breed dogs have the shortest average lifespan, at 810 years. Unfortunately, a 6-year-old Great Dane is considered a senior pet, given the wear-and-tear their joints experience. Giant breeds are also far more prone to bone cancers and neurologic diseases than smaller dogs.
Here are some popular large dog breeds and their average lifespans:
How to Help Your Dog Live Longer
Do Your Research
Because dog lifespans are so breed-dependent, if youre interested in a certain breed its extremely important to research carefully and select a responsible breeder who is invested in their dogs health. Responsible breeders will test for common diseases in their breeding dogs (both health screening and genetic tests are available for many common issues). Knowing the lifespan and health concerns of your puppys relatives can help you make an informed decision.
While mixed-breed dogs may live longer than some breeds, many designer breeds (like Goldendoodles and Labradoodles) initially created to be healthier are now bred to the point of having their own specific issues. So, these breeders should be held to the same standards.
Mixed-breed dogs from shelters often have a variable enough pedigree that they are not subject to the same risks as designer breeds. But because breed-specific illnesses can still arise, it can be worthwhile for pet parents to DNA test their shelter pup, as many of these DNA tests will also look for evidence that your dog has the genes for common diseases. So, by knowing more about your dogs background, you can anticipate some issues that may come up.
Follow Your Vets Guidance
Its important to follow to your veterinarians preventative health recommendations. Vaccinationsas well as location-appropriate flea, tick, and heartworm preventionwill protect your pet against communicable diseases.
Routine testing for intestinal and blood parasites should be done on an annual basis. Discuss routine bloodwork panels to check liver, kidney, and bone marrow health with your veterinarian as well. Establishing baselines in young dogs and checking them annually as they get older can help you find diseases early when they are more easily managed. Keep in mind, senior dogs should have more testing done as they age to check for additional age-related issues that may arise.
Some breeds, like Golden Retrievers, may benefit from routine imaging (X-rays and ultrasounds) as they age to monitor for certain types of cancer.
Keep Your Dog at a Healthy Weight
A healthy weight is essential for a long-lived dog. A study of Labrador Retrievers found that dogs kept at a healthy body condition lived an average of two years longer than their overweight counterparts.
Feed your dog in measured meals and keep track of treats and snacks so that you can appropriately adjust their intake as their metabolism changes. If you are unsure your dog is a healthy weight, thats a great question for your veterinarian.
Featured Image: iStock/Halfpoint
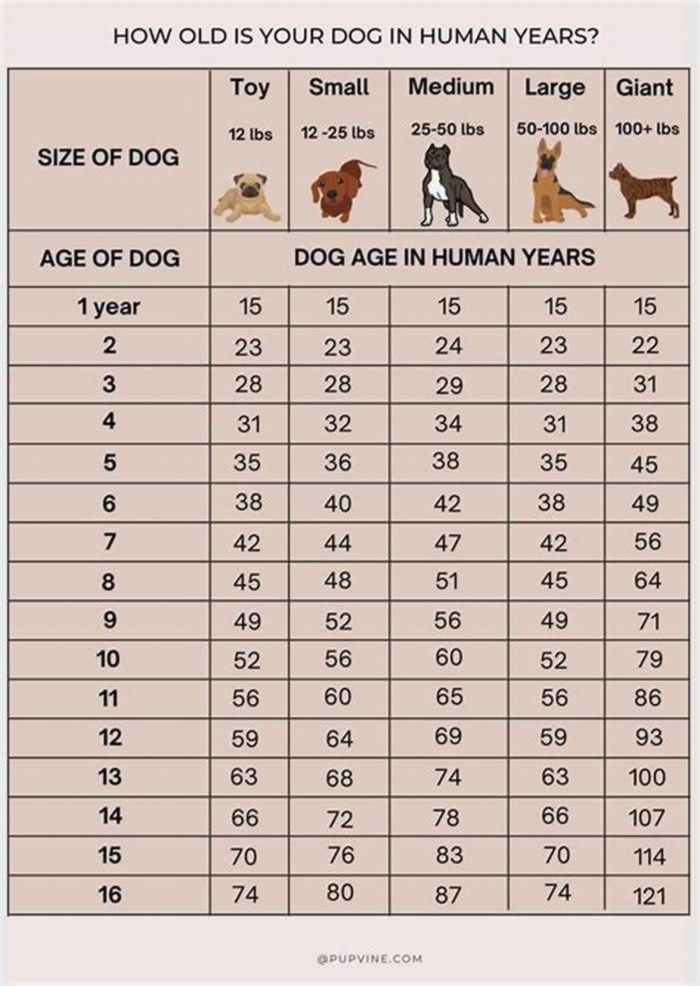
How to Calculate Dog Years to Human Years
Since the 1950s, the popular calculation of how old a dog was in human years has been that one dog year is the equivalent of seven human years. Even though this formula has been around for a surprisingly long time, the reality is not so cut-and-dried. That doesnt stop people from defaulting to this traditional calculation. You cant really kill the seven-year rule, says Kelly M. Cassidy, a curator of the Charles R. Connor Museum at Washington State University, who compiles studies about longevity in dogs.
One explanation for how this formula got started is that the 7:1 ratio seems to have been based on the statistic that people lived to about 70, and dogs to about 10.
My guess is it was a marketing ploy, says William Fortney, a veterinarian at Kansas State University. He tells the Wall Street Journal that it was a way to educate the public on how fast a dog ages compared to a human, predominantly from a health standpoint. It was a way to encourage owners to bring in their pets at least once a year.
How toCalculate Dog Years to Human Years?
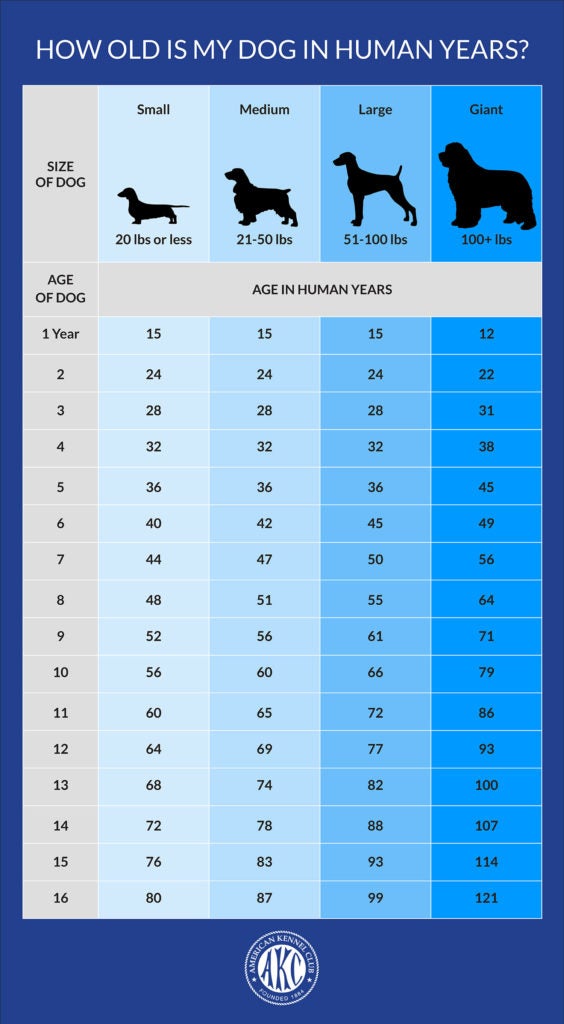
As a general guideline, though, the American Veterinary Medical Association breaks it down like this:
- 15 human years equals the first year of a medium-sized dogs life.
- Year two for a dog equals about nine years for a human.
- And after that, each human year would be approximately five years for a dog.
How Do Researchers Come Up With Those Numbers?
There are many several factors to consider, so its not possible to pin it down precisely, but the AVMA says: Cats and small dogs are generally considered senior at seven years old, but we all know theyve got plenty of life left in them at that age. Larger-breed dogs tend to have shorter lifespans compared to smaller breeds and are often considered senior when they are 5 to 6 years of age. The senior classification is based on the fact that pets age faster than people, and veterinarians start seeing more age-related problems in these pets. Contrary to popular belief, dogs do not age at a rate of 7 human years for each year in dog years.
An example would be the Great Dane. The average life expectancy, according to the Great Dane Club of America, is about 710 years. Therefore, a 4-year-old Great Dane would already be 35 in human years. Again, keep in mind that these are rough estimates.
The National Center for Health Statistics doesnt keep records for dogs. Instead, there are three main sources for data on their longevity: pet-insurance companies, breed-club surveys, and veterinary hospitals.
Why DoSmaller Dogs Live Longer than Larger Dogs?
This phenomenon has baffled scientists for years, and research has yet to explain the relationship between body mass and a dogs lifespan.
Generally speaking, large mammals, like elephants and whales, tend to live longer than small ones, like mice. So why do small dogs have a longer average life span than large breeds?
Large dogs age at an accelerated pace, and their lives seem to unwind in fast motion, according to researcher Cornelia Kraus, an evolutionary biologist at the University of Gttingen in Germany, speaking to Inside Science. Scientists concluded that every 4.4 pounds of body mass reduced a dogs life expectancy by about a month. The reason why is still unknown, though Kraus puts forward several possibilities, including that larger dogs may succumb to age-related illnesses sooner and that the accelerated growth of large dogs may lead to a higher likelihood of abnormal cell growth and death from cancer. Scientists plan future studies to better explain the link between growth and mortality.

Canine gerontology is a burgeoning field of science, as dog lovers are looking to not only extend the time they have with their pets, but to improve the quality of that time. The Dog Aging Project is studying the aging process in dogs, using geroscience research to delay aging and promote healthy longevity.
Whether measured in human years or dog years, as our dogs mature and age there is beauty and charm at every step along the way. With their gray muzzles and wise expressions, senior dogs are especially lovable and poignant.
2019 Epigenetic Clock Study
A2019 studyby researchers at the University of California San Diego put forth a new method for calculating dog age, based on changes made to human and dog DNA over time. In both species, methyl groups are added to DNA molecules throughout aging, altering DNA activity without altering the DNA itself. As a result, DNA methylation has been used by scientists to study aging in humans through an epigenetic clock.
The research team performed targeted DNA sequencing in 104 Labrador Retrievers spanning a 16 year age range, in an attempt to compare dogs epigenetic clocks to those of humans. The results allowed them to derive a formula for adjusting dogs ages to human years, by multiplying the natural logarithm of the dogs age by 16 and adding 31 (human_age = 16ln(dog_age) + 31).Thisnatural logarithm calculatorcan help.
As the study included just a single breed, your own dogs human age based on this formula may not quite match up. Its known that different breeds age differently, so the UCSD formula may lack enough variables for conclusive results. Regardless, the new science-backed formula put forth is certainly more useful to those looking to calculate dogs human age than the long-debunked multiply by 7 myth.
Did You Know?
Evidently, people have been comparing human-to-dog years for centuries.
In 1268, the artisans creating the Cosmati Pavement in Westminster Abbey inscribed into the floor a prediction for Judgement Day: If the reader wisely considers all that is laid down, he will find here the end of the primum mobile; a hedge lives for three years, add dogs and horses and men, stags and ravens, eagles, enormous whales, the world: each one following triples the years of the one before.
By this math, a dog lives to nine, a man to 80. If these statistics were accurate, between 1268 and the mid-20th century, dogs had a year trimmed off their lifespan, and we lost almost a decade. Luckily for both species, our lifespans have gone in the other direction.
If you are the proud owner of a senior dog, celebrate the love they give you with senior dog toys, hip & joint treats, and comfy orthopedic dog beds to make their golden years the best ever.